- 2017/2019- iNOVA4HEALTH Project 35: 2015\CEDOC\IPOLFG\IBET
Targeting monocytes as angiogenesis promoters in cancer- New application for old drugs.
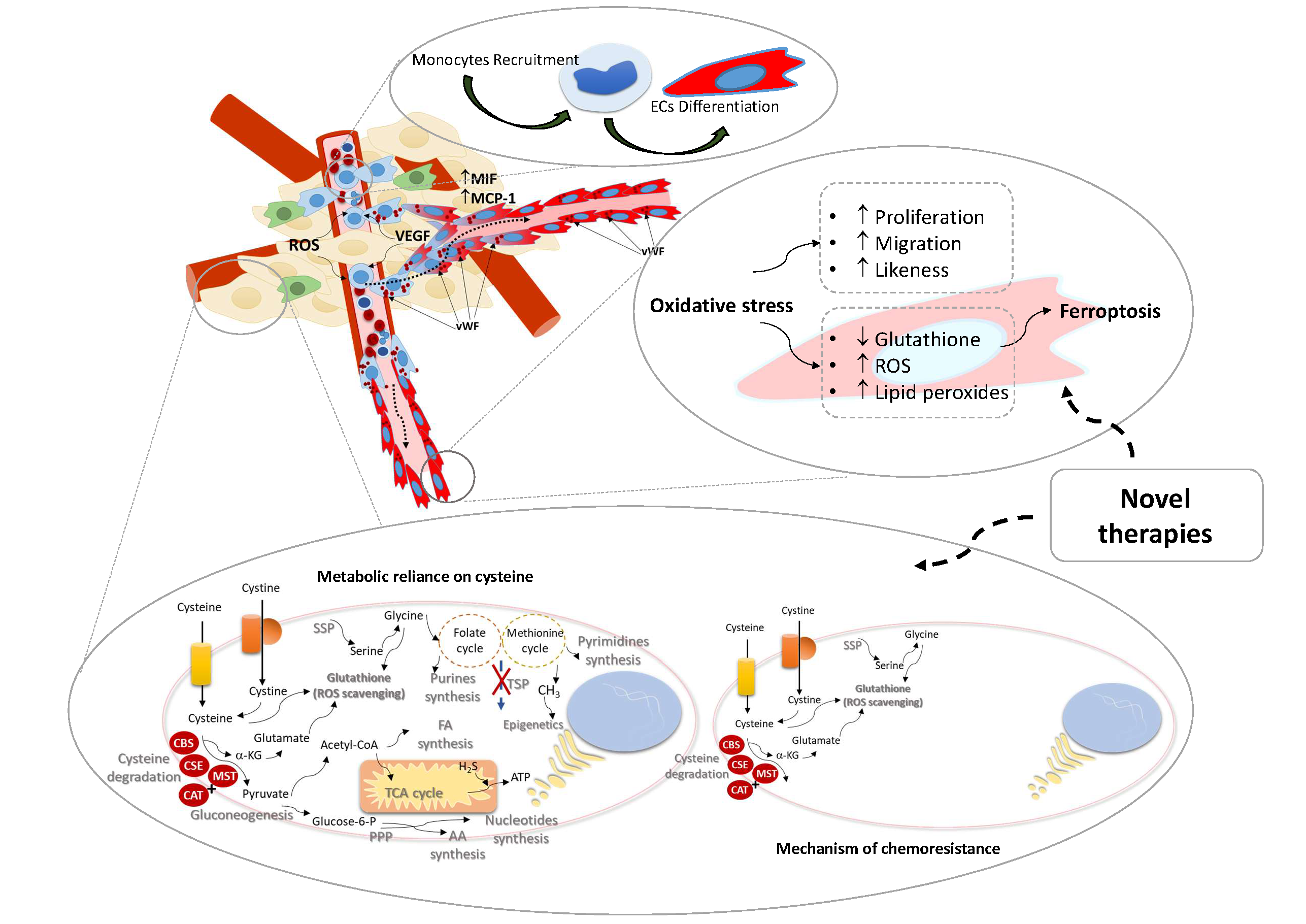
The role of monocytes as endothelial precursors is not a new subject in other diseases, but in cancer this issue was not extensively studied. Studies showed that a subset of circulating monocytes are capable of in vitro EC differentiation, and in vivo incorporation in new blood vessels, in cancer. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are reported as essential in endothelium homeostasis, acting as regulators of intracellular signaling.
Moreover, it is known that some drugs (i.e. β-blockers), already approved for human use, have simultaneously a pro-apoptotic role in EC and a modulatory role in monocytes differentiation.
Our hypothesis is that monocytes are relevant endothelial precursors and the manipulation of oxidative stress with the use of some drugs can be a new weapon to control cancer angiogenesis.
Our main goals are to disclose monocytes as endothelial precursors, unravel the role of oxidative stress in angiogenesis and take advantage of redox state to control vessels growth.
Publications:
Lopes-Coelho F, Silva F, Hipólito A, Mendes C, Sequeira CO, Pires RF, Almeida AM, Bonifácio VDB, Pereira SA, Serpa J. The activation of endothelial cells relies on a ferroptosis-like mechanism: novel perspectives in management of angiogenesis and cancer therapy. Front. Oncol., 10 May 2021. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.656229.
Lopes-Coelho F, Silva F, Gouveia-Fernandes S, Martins C, Lopes N, Domingues G, Brito C, Almeida AM, Pereira SA, Serpa J. Monocytes as Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPCs), Another Brick in the Wall to Disentangle Tumor Angiogenesis. Cells. 2020 Jan 1;9(1):107. doi: 10.3390/cells9010107.
- 2015/2017- iNOVA4HEALTH Project 4: 2015\CEDOC\IPOLFG\IBET
Ovarian cancer a suitable model to define metabolic profile as a tool to predict chemoresistance
EOC is a natural model to study therapy resistance. Approximately 70% of patients have extraovarian disease and besides the initial response to therapy, over 60% have recurrence of disease and the mortality rate is 70-90%, mainly due to chemoresistance. We published a study that shows, in ovarian clear cell carcinoma, that amino acids metabolism and glutathione production underlie the intrinsic resistance of this histological cancer type to carboplatin.
Thus, alterations in metabolic profile induced by exposure to chemotherapy can be an useful tool to predict, anticipate and abrogate chemoresistance in ovarian cancer patients.
The main objective is to use the ovarian cancer model to evaluate the impact of metabolic fitness in chemoresistance.
Publications:
Nunes SC, Ramos C, Santos I, et al. Cysteine Boosts Fitness Under Hypoxia-Mimicked Conditions in Ovarian Cancer by Metabolic Reprogramming. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 11;9:722412. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.722412.
Santos I, Ramos C, Mendes C, et al.. Targeting Glutathione and Cystathionine β-Synthase in Ovarian Cancer Treatment by Selenium-Chrysin Polyurea Dendrimer Nanoformulation. Nutrients. 2019 Oct 19;11(10):2523. doi: 10.3390/nu11102523.
Nunes SC, Ramos C, Lopes-Coelho F, et al.. Cysteine allows ovarian cancer cells to adapt to hypoxia and to escape from carboplatin cytotoxicity. Scientific Reports. 2018 Jun 22;8(1):9513. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27753-y.
Nunes SC, Lopes-Coelho F, Gouveia-Fernandes S, et al.. Cysteine boosters the evolutionary adaptation to CoCl2 mimicked hypoxia conditions, favouring carboplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. BMC Evololutionary Biology 2018 Jun 19;18(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12862-018-1214-1.